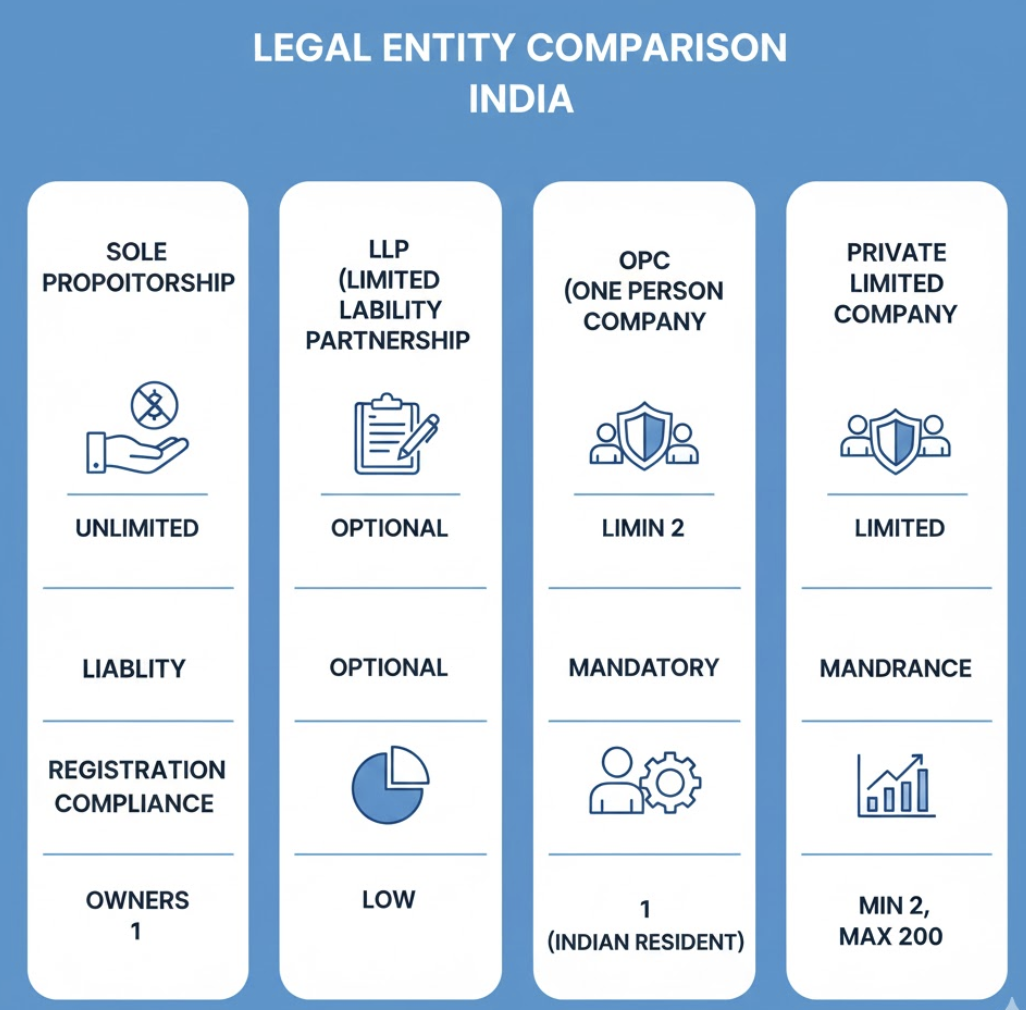
When entrepreneurs begin their journey, one of the first and most important decisions they face is choosing among the Types of Business Structures in India. This choice impacts taxation, compliance, ownership, liability, investor trust, and even day-to-day operations.
Many new founders rush into a structure without understanding its long-term implications. However, selecting the correct structure early on can save significant time, cost, and legal complexity down the road. In this article, we break down each structure in a founder-friendly way, offering clarity and real-world examples so you can make an informed decision.
Let’s explore all Types of Business Structures in India, their pros, cons, and ideal use cases.
Sole Proprietorship – The Simplest Business Structures in India
A Sole Proprietorship is the easiest structure to start in India. It is not a separate legal entity; instead, the business and the owner are considered the same.
✔ Pros
- Easiest to start with almost no formal registration
- Full control with zero interference
- Very low compliance and tax filings
- Ideal for small traders, freelancers, and home businesses
✘ Cons
- Unlimited personal liability
- Cannot raise equity funding
- Not recognized by investors or large corporations
- Difficult to scale
Best for: Freelancers, consultants, individual service providers, local shops.
Partnership Firm – Easy to Start but High Liability
A Partnership Firm is formed when two or more people start a business together through a partnership deed.
✔ Pros
- Easy to form with minimal legal requirements
- Low cost and low compliance
- Suitable for small family businesses
✘ Cons
- Unlimited liability for all partners
- Legal disputes between partners can complicate business
- Not suitable for raising funds
- Not ideal for modern startups
Best for: Small family businesses, trading businesses, local service providers.
LLP (Limited Liability Partnership) – Liability Protection with Flexibility
An LLP blends the advantages of a partnership and a company. It offers limited liability, meaning partners are not personally responsible for business debts.
✔ Pros
- Limited liability protects personal assets
- Moderate compliance, lower than a Private Limited
- Flexible internal management
- No minimum capital requirement
✘ Cons
- Not preferred by angel investors or VCs
- Some restrictions on raising funds and issuing shares
- Higher compliance than a partnership firm
Best for: Consultants, agencies, law firms, and professional service providers.
Private Limited Company – The Most Popular Business Structures in India
Among all Types of Business Structures in India, the Private Limited Company stands out as the most trusted and scalable option.
✔ Pros
- Limited liability protection
- Eligible for investment from angels, VCs, and institutions
- Strong credibility with banks and customers
- Ability to issue shares and ESOPs
- Mandatory for businesses planning to scale
✘ Cons
- Higher compliance and audit requirements
- Registration process is more detailed
- Costs are slightly higher than LLP or sole proprietorship
Best for: Startups, scalable businesses, tech companies, SaaS, D2C brands, funded ventures.
One Person Company (OPC) – Perfect for Solo Founders
An OPC allows a single founder to register a company with limited liability.
✔ Pros
- Ideal for solo entrepreneurs
- Reduced compliance compared to a Private Limited
- Full control with corporate structure
- Separate legal identity
✘ Cons
- Restricted on certain business activities
- Not suitable for venture capital
- Mandatory conversion after turnover/paid-up capital limits
Best for: Solo business owners, consultants, freelancers transitioning to corporate structure.
Section 8 Company : For Non-Profits
A Section 8 Company is registered for charitable purposes such as education, arts, sports, environment, or social welfare.
✔ Pros
- Tax exemptions and government benefits
- High credibility for NGO activities
- Separate legal identity
✘ Cons
- Profit distribution is not allowed
- Strict compliance structure
Best for: NGOs, CSR programs, educational or social enterprises.
Public Limited Company – For Large, Growing Enterprises
A Public Limited Company allows raising capital from the public and listing on stock exchanges.
✔ Pros
- Ability to raise large-scale funding
- High credibility and transparency
- Essential for companies planning IPOs
✘ Cons
- Very high compliance
- Requires minimum directors, shareholders, and regulatory oversight
Best for: Large corporations, enterprises aiming for IPO.
Feature-by-Feature Comparison of Business Structures in India
| Structure | Liability | Compliance | Fundraising Ability | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sole Proprietorship | Unlimited | Very Low | None | Freelancers, small shops |
| Partnership | Unlimited | Low | Limited | Family businesses |
| LLP | Limited | Medium | Low | Agencies, professionals |
| Private Limited | Limited | High | Excellent | Startups, scalable businesses |
| OPC | Limited | Medium | Low | Solo entrepreneurs |
| Section 8 | Limited | High | Grants, donations | NGOs |
| Public Ltd | Limited | Very High | Very High | Large enterprises |
How to Choose the Right Structure Based on Your Goals
Here’s a quick framework:
✔ If you want to start small and simple
→ Sole Proprietorship or Partnership Firm
✔ If you want limited liability with low compliance
→ LLP
✔ If you want to raise investment or scale
→ Private Limited Company
✔ If you are a solo entrepreneur
→ OPC or Sole Proprietorship
✔ If you plan to run a non-profit
→ Section 8 Company
✔ If long-term vision includes IPO
→ Public Limited Company
🧾 Conclusion: Different Structures for Different Dreams
India offers a wide variety of business structures because no two businesses are alike. While small businesses may thrive with a simple model like Sole Proprietorship, ambitious startups often choose Private Limited Companies to scale faster.
Understanding the Types of Business Structures in India ensures you avoid costly mistakes and build on the right foundation. As your business grows, the right structure will support you in taxation, compliance, investment, and expansion.
If you want, I can now proceed with Series 1 – Article 3:
Private Limited vs LLP vs OPC vs Sole Proprietorship – Which Is Best for You?
❓ FAQs
1. What is the most common Business Structures in India?
The Private Limited Company is the most preferred structure, especially for startups and scalable businesses.
2. Which Business Structures in India is best for freelancers?
A Sole Proprietorship or OPC suits freelancers depending on revenue and liability concerns.
3. What is the easiest Business Structures in India to register?
A Sole Proprietorship is the easiest; however, it offers no liability protection.
4. Can a single person start a company in India?
Yes, through a One Person Company (OPC) or Sole Proprietorship.
5. Which Business Structures in India is best for raising investment?
Only a Private Limited Company is preferred by investors.
Read Article 1: Choosing the Right Business Structure in India
Read all articles :- Company Registration in India – Complete Article Series Topics
MCA (Official Government Portal): https://www.mca.gov.in/